Hungarian competitiveness is practically stagnant, after 47.4 in 2020, we score 47.6 in the Multinational Group Competitiveness Report – From a document submitted on Wednesday. This puts us 18th in the European Union, according to a report by the Central Bank, an improvement over last year, but only because of Brexit, the UK is no longer on the list. More details:
General results for banks
More general findings about banks in the Competitiveness Report:
- Ensuring the availability of effective and stable bank financing is essential to maintaining domestic economic convergence.
- While in the corporate sector the domestic banking system can be placed in the middle of the EU in terms of pricing, on the retail side there is moderate competition for APR-based installments on housing loans.
- For all sectors and loan products, the predictability of installments should be pursued.
- In order to maintain the long-term role of the banking system in supporting the economy, it is necessary to have a strong capacity to raise and attract capital and to avoid the accumulation of systemic stability risks.
- Digital presence is also an increasingly important competitive advantage in the provision of financial services, while Covid19 has also highlighted the importance of resilience arising from digital operations.
- In addition to the digital transformation of existing financial institutions, the existence and development of an advanced financial technology ecosystem and the institutional and legal environment that supports it is also of paramount importance.
More specific results
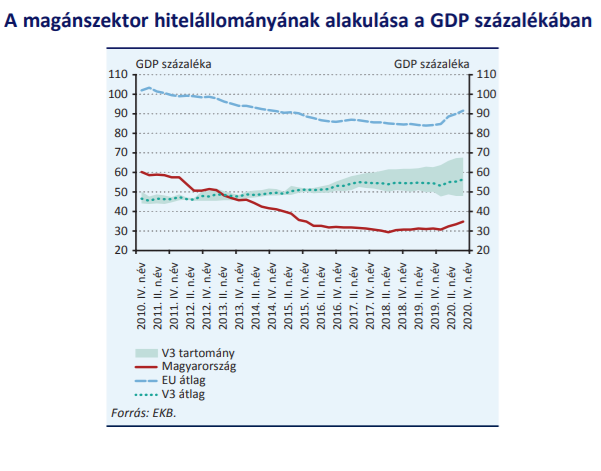
In 2020, due to the central bank and government loan programs and the moratorium on payment, the private sector loan portfolio continued to expand and GDP declined, so that its level as a share of GDP already by the end of 2020 exceeded 35 percent after the previous one. The level is about 30 percent. However, this value remains as a significant reserve for further expansion of prudent lending.
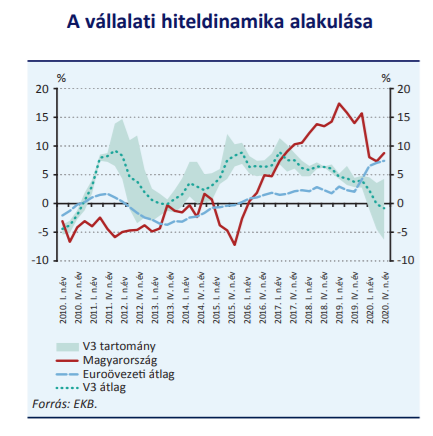
At the end of the first quarter of 2020, the coronavirus epidemic reached Hungary with annual corporate loan dynamics exceeding 15 percent, which subsequently decreased to nearly 9 percent by the end of 2020 due to the negative effects of the virus on the economy. . However, lending cannot be considered overheated.
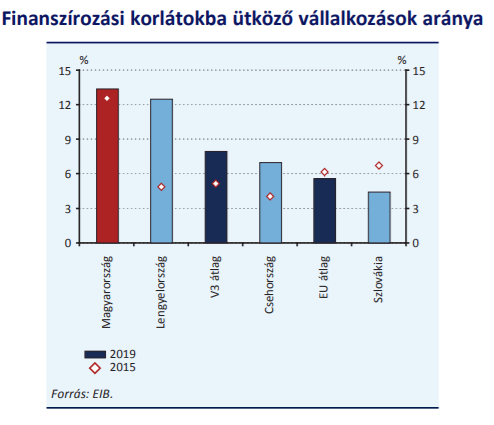
According to an investment survey conducted by the European Investment Bank, in fiscal year 2019, nearly 6 per cent of companies operating in the EU, while more than 13 per cent of Hungarian companies, faced funding constraints. As a result of a deterioration of nearly 5 percentage points compared to 2018, local companies faced the level of the financing limit experienced in 2015. There is room for improvement, according to the Central Bank, by diversifying financing channels and improving the efficiency of the institutional guarantee system.
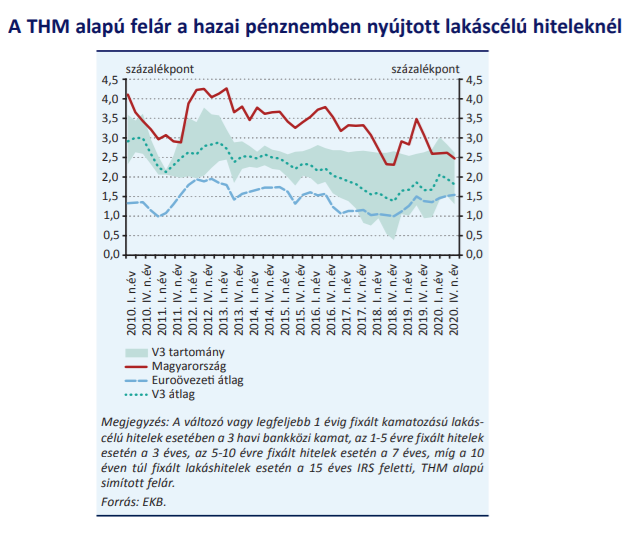
The spread of domestic housing loans continues to exceed the average of the euro area and other Visegrad countries. In 2020, despite higher benchmark yields, lending rates fell, which led to an overall decline in margins. With this we have reached the top of the Visegrad countries again. At the end of 2020, the average interest rate differential for domestic housing loans was 2.5 percentage points, which is 60 basis points lower than the same period a year earlier.
As a result of the FGS Fixed Scheme launched in 2019, the share of fixed rate loans has returned to the required level above 50 per cent, and as a result of the launch of FGS Hajra in April 2020, in lending.
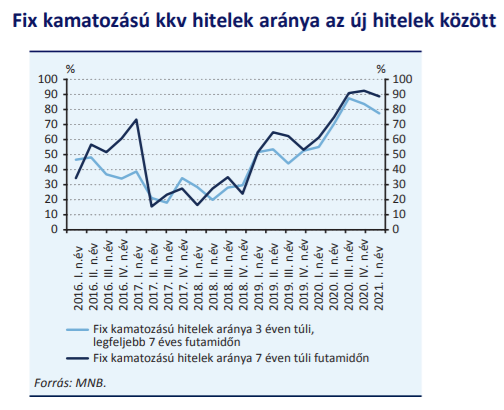
While at the beginning of 2016, the share of floating rate loans in the issuance of new housing loans was still 42 percent, by the end of 2019, consumer-friendly housing loans (MFL) and differentiation into high-risk loans had been introduced. As a result, by the end of 2020, the share of floating rate retail mortgages in the portfolio had fallen to 40 percent from 70 percent in 2016.
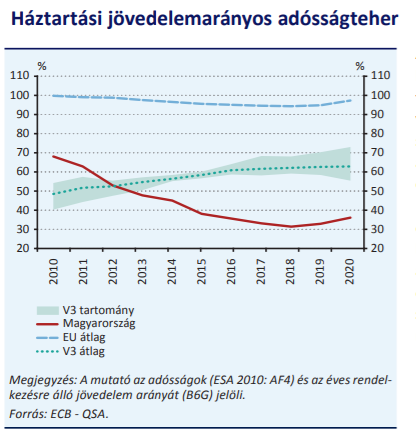
The ratio of domestic debt to income is one of the lowest in the European Union, and even a large compensation reserve can be set compared to other Visegrad countries, the Central Bank countries.
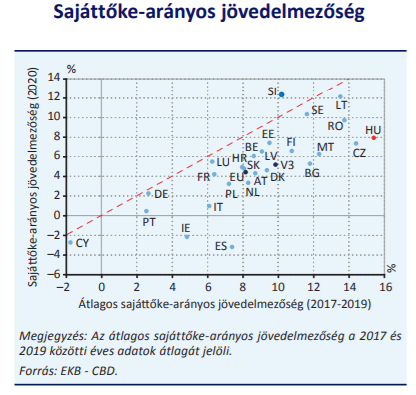
From 2017 to 2019, partly due to a reversal of previously configured declines, the domestic sector has always been on the podium in the EU with its outstanding profitability, with fifth place in return on equity in 2020 still positive.
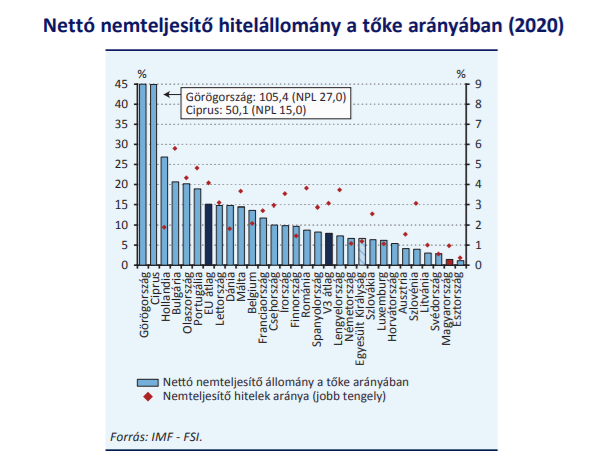
The NPL ratio remained largely supported by the repayment suspension that was introduced and extended in March 2020, both by preventing new delays and positively impacting overall credit growth, but the increased credit risk is reflected in the increase in Phase 2 loans and increased coverage for impairment.
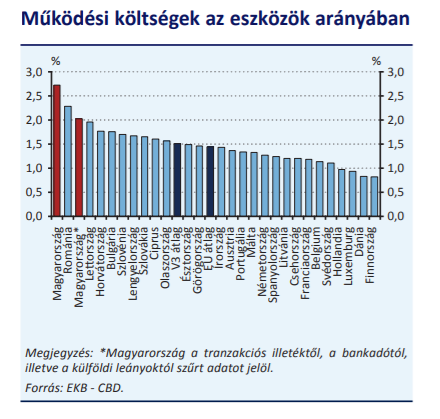
Pending operating costs are a constraint on profitability and pricing of banking products. Competitiveness reserve is found in all sub-items – personnel expenses, administrative expenses, and depreciation. Since the second half of 2019, asset-based operating costs for the consolidated segment have fallen in a trend-like fashion, with collaborative integration contributing significantly, but with the expansion of financial penetration and digitalization, there is still room for improvement.
Cover Photo: Getty Images








More Stories
Despite economic hardships, 85% of companies are increasing their investment in cloud solutions
Viktor Orban plans to lead Hungary until 2040 – everything in one place about PM’s speech in Tosvany
Companies have to do a lot of work if they don’t want to cook their employees